Historical Evolution of NATO Membership
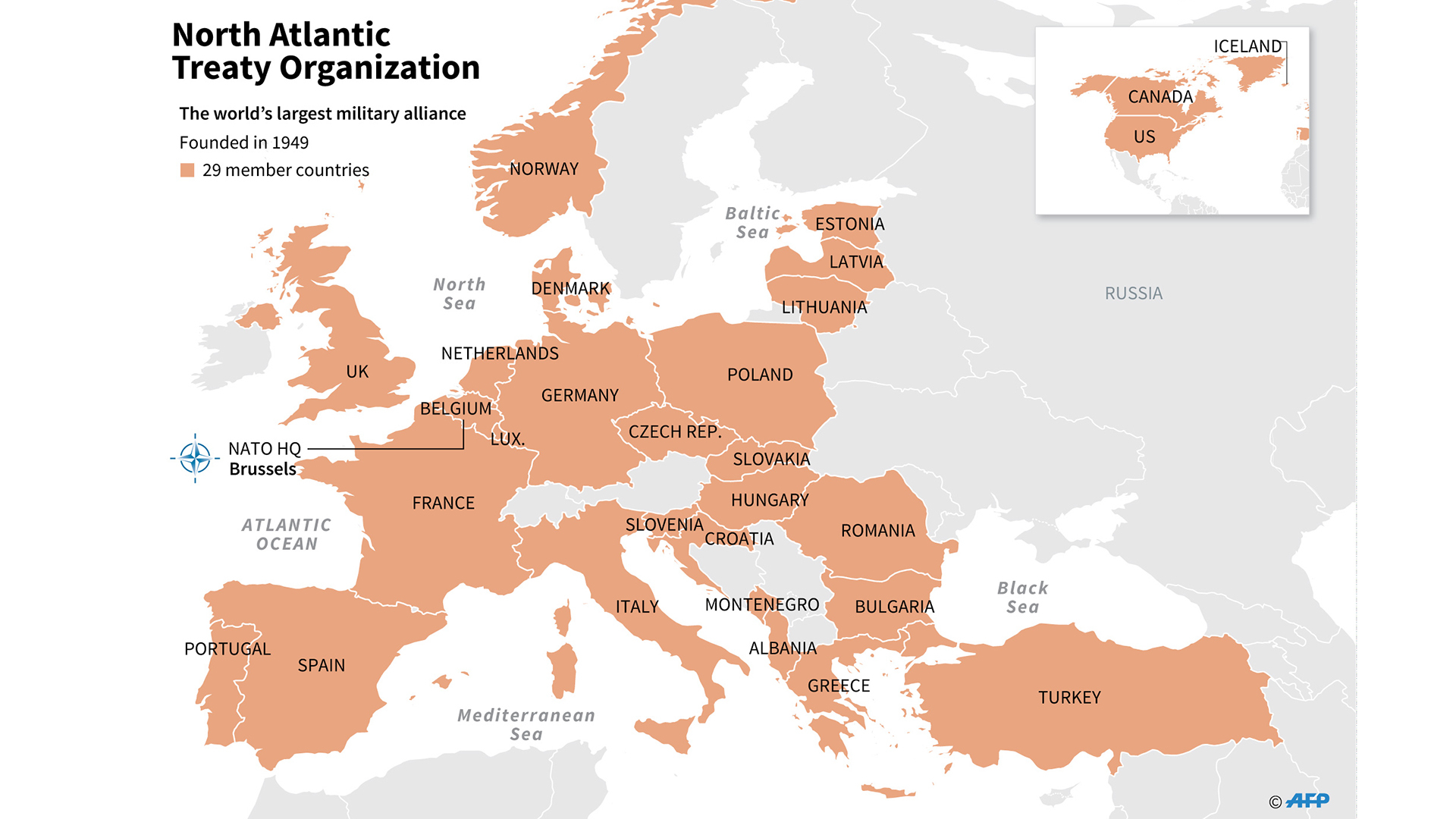
Nato members – The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) has undergone significant expansion since its inception in 1949, with the addition of new members reflecting changing geopolitical dynamics and strategic considerations.
NATO members have been expressing concerns about Russia’s aggression in Ukraine, and US President Joe Biden recently addressed these concerns in an ABC interview. Biden emphasized the importance of NATO unity and reaffirmed the US commitment to defending its allies.
The interview provided reassurance to NATO members and demonstrated the Biden administration’s determination to uphold the alliance.
NATO’s expansion has been driven by several factors, including the need to strengthen the alliance’s collective defense capabilities, promote stability in Europe, and respond to emerging threats.
First Wave of Expansion (1952-1955)
- Greece and Turkey joined NATO in 1952, bolstering the alliance’s southern flank during the Cold War.
- West Germany joined in 1955, symbolizing its reintegration into the Western bloc.
Second Wave of Expansion (1982-1990)
- Spain joined NATO in 1982, expanding the alliance’s presence in the Mediterranean.
Post-Cold War Expansion (1999-2009), Nato members
- Poland, Hungary, and the Czech Republic joined NATO in 1999, marking the alliance’s first eastward expansion.
- Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Romania, and Bulgaria joined in 2004.
- Albania and Croatia joined in 2009.
Recent Expansion (2017-Present)
- Montenegro joined NATO in 2017.
- North Macedonia joined in 2020.
Current NATO Membership and Its Implications

The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) currently comprises 30 member states, each contributing to the alliance’s collective security and defense. These member states represent a diverse range of geopolitical regions, military capabilities, and economic strengths, offering NATO a broad spectrum of resources and perspectives.
Member State Contributions
NATO member states contribute to the alliance in various ways. The United States, as the leading military power within NATO, provides significant financial and military resources, including advanced weaponry, intelligence sharing, and troop deployments. Other major contributors include the United Kingdom, France, Germany, and Canada, which offer specialized capabilities in areas such as naval warfare, air defense, and cyber operations.
Smaller member states also play crucial roles within NATO. For instance, the Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania) contribute to the alliance’s eastern flank defense, while Portugal provides access to the Atlantic Ocean for NATO operations. Additionally, newer members such as Montenegro and North Macedonia enhance NATO’s presence in the Balkans and promote regional stability.
Impact on Security and Stability
NATO membership has a profound impact on the security and stability of its member nations. The alliance’s collective defense guarantee, enshrined in Article 5 of the Washington Treaty, provides member states with a sense of assurance that they will not be left alone in the face of aggression. This guarantee has been instrumental in deterring potential adversaries and preventing armed conflicts within the NATO area.
Moreover, NATO membership fosters cooperation and coordination among member states, enabling them to address common security challenges. Through joint exercises, training, and information sharing, NATO members enhance their interoperability and ability to respond effectively to threats such as terrorism, cyberattacks, and hybrid warfare.
Challenges and Opportunities
NATO’s diverse membership presents both challenges and opportunities for the alliance. On the one hand, the inclusion of member states with varying perspectives and interests can sometimes lead to disagreements and differing priorities. Balancing these diverse interests requires effective diplomacy and consensus-building within NATO.
On the other hand, NATO’s diversity also provides the alliance with a wide range of expertise and capabilities. By harnessing the unique strengths of its member states, NATO can adapt to evolving security threats and address complex challenges that no single nation could tackle alone.
As NATO continues to evolve and adapt to the changing global landscape, the alliance’s diverse membership will remain a key factor in its ability to maintain its relevance and effectiveness as a guarantor of Euro-Atlantic security.
Prospective NATO Membership and Its Potential

NATO’s expansion has been a contentious issue since the end of the Cold War, with some arguing that it has increased stability in Europe while others believe it has provoked Russia and undermined its security. The debate over NATO enlargement is likely to continue for many years to come, as there are a number of countries that are interested in joining the alliance.
One of the most frequently discussed potential NATO members is Ukraine. Ukraine has been a partner of NATO for many years, and it has expressed a desire to join the alliance since the early 2000s. However, Ukraine’s membership bid has been met with resistance from Russia, which sees NATO expansion as a threat to its security.
Another potential NATO member is Georgia. Georgia has also been a partner of NATO for many years, and it has also expressed a desire to join the alliance. However, Georgia’s membership bid has also been met with resistance from Russia, which sees NATO expansion as a threat to its security.
In addition to Ukraine and Georgia, there are a number of other countries that have expressed an interest in joining NATO. These countries include Bosnia and Herzegovina, Macedonia, and Montenegro. However, it is unclear whether these countries will be able to join NATO in the near future, as there are a number of obstacles that they must overcome.
Strategic Implications of Expanding NATO’s Membership
The strategic implications of expanding NATO’s membership are complex and far-reaching. On the one hand, NATO expansion could help to promote stability in Europe by deterring Russian aggression. On the other hand, NATO expansion could also provoke Russia and lead to a new arms race.
The potential benefits of NATO expansion include:
– Deterrence of Russian aggression: NATO expansion could help to deter Russian aggression by making it clear that any attack on a NATO member would be met with a collective response from the entire alliance. This could help to prevent Russia from using military force to achieve its political goals.
– Promotion of stability in Europe: NATO expansion could help to promote stability in Europe by creating a more secure and stable environment for all countries in the region. This could help to reduce the risk of conflict and promote economic growth.
The potential risks of NATO expansion include:
– Provocation of Russia: NATO expansion could provoke Russia and lead to a new arms race. Russia sees NATO expansion as a threat to its security, and it has responded by increasing its military spending and developing new weapons systems. This could lead to a new arms race and increase the risk of conflict between Russia and NATO.
– Undermining of the OSCE: NATO expansion could undermine the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE). The OSCE is a regional security organization that includes both NATO members and non-NATO members. NATO expansion could lead to the OSCE becoming less effective, as non-NATO members may be less willing to cooperate with an organization that is seen as being dominated by NATO.
Geopolitical Dynamics that Could Influence the Decision-Making Process for Future NATO Expansion
The geopolitical dynamics that could influence the decision-making process for future NATO expansion are complex and ever-changing. Some of the most important factors that could influence the decision-making process include:
– The relationship between Russia and NATO: The relationship between Russia and NATO is one of the most important factors that will influence the decision-making process for future NATO expansion. If Russia continues to see NATO expansion as a threat to its security, it is likely to continue to oppose any further enlargement of the alliance.
– The political situation in the Western Balkans: The political situation in the Western Balkans is another important factor that could influence the decision-making process for future NATO expansion. If the Western Balkans remains unstable, it is likely that NATO will be reluctant to expand into the region.
– The rise of China: The rise of China is another important factor that could influence the decision-making process for future NATO expansion. If China continues to grow in power and influence, it is likely that NATO will need to adjust its strategy to take into account the changing balance of power in the world.